Soap (used in your bathroom and kitchen) is a cleaning agent made by combining grease or oil with an alkali (such as sodium hydroxide). This process is called saponification, and it creates molecules that can hold onto both water and grease, which greatly helps wash away dirt and oil. Next, we will also learn soap making process.
Raw Materials.
Tallow is the principle fatty material in soap making process . it contain mixed glycerides obtained from the solid fat of cattle. This solid fat is digested with stem. The tallow forms a layer above water and is easily removed.
Tallow is usually mixed with coconut oil to increase the solubility of soap. Greases are also used as raw material for soap making. these are important source of glycerides of fatty acids. The soap made from coconut oil lathers well. Inorganic chemicals added to soap are called builders e.g., soda ash, sodium tripolyphosphate, tetrasodium pyrophosphate.
Process of manufacture.
Soap is made by the saponification of glycerides of fatty acids.. The basic chemical reaction in soap making Process is saponification of fat.
(CH17H35COO)3C3H5 + 3NaOH → 3C17H35COONa + C3H5(OH)3
The following two steps are involved in soap making:
The fat is hydrolyzed to get fatty acid and glycerine. The fatty acid is neutralized with caustic soda solution to form soap.
(CH17H35COO)3C3H5 + 3H2O → 3C17H35COOH + C3H5(OH)3
CH17H35COOH + NaOH → 3C17H35COONa + H2O
The fatty oil is deaerated under vacuum to prevent darkening through oxidation during processing.. It is charged at a controlled rate to the bottom of the hydrolyzing tower, which breaks the fat into droplets. These towers are about 20 m high and 60 cm in diameter and are made of stainless steel. At the same time deaerated, demineralised water is fed to the top of contacting section to separate glyerine from fatty phase. They fatty acids are discharged from the top of the hydrolyser to a decanter and glycerine – water solution from the bottom. The melted fatty acids are swirled in a pan and neutralized with 50% caustic soda to obtain soap..
The neat soap is discharged at 93° C into blending tank and extruded, milled, flaked or spray – dried. The soap is heated at about 200 ° C under high pressure steam exchanger. The heated soap is released to a flash tank atmospheric pressure, where partial drying takes place. The soap is cooled from 105 ° C to about 65 ° C and cut into bar lengths.
The main classes of soap are toilet soaps and industrial soap. All soaps contain 10-30 ° C water. if soap anhydrous, it would be too hard to dissolve it. Toilet soaps contain 10-15 % moisture and have perfume and a fraction of a percent of titanium dioxide as a whitening agent. shaving soaps are potassium salts of mainly steric acid.
Saponification.
Saponification is an interesting chemical reaction. This is the reaction we use to make soap. The name may seem a bit complicated, but it’s very easy to understand.
What is Saponification.
Saponification means making soap. This is a chemical reaction that occurs when we combine fat or oil with a strong base (such as sodium hydroxide – NaOH).
When fat and base react, two things are formed:
- Soap (which is the sodium salt of a fatty acid)
- Glycerol (by-product, which we use in creams and lotions).
Chemical Reaction.
Fat/Oil + NaOH → Soap (Sodium salt of fatty acid) + Glycerol
For example:
If we heat triglycerides (fats) with NaOH, we get sodium stearate (which is a type of soap) and glycerin.
Importance of Saponification.
- This reaction happens to him in daily life – this is the basic process in soap factories.
- Glycerol, which is a side product, is found in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
- This process is an example of organic chemistry – in which carbon compounds react to form useful substances.
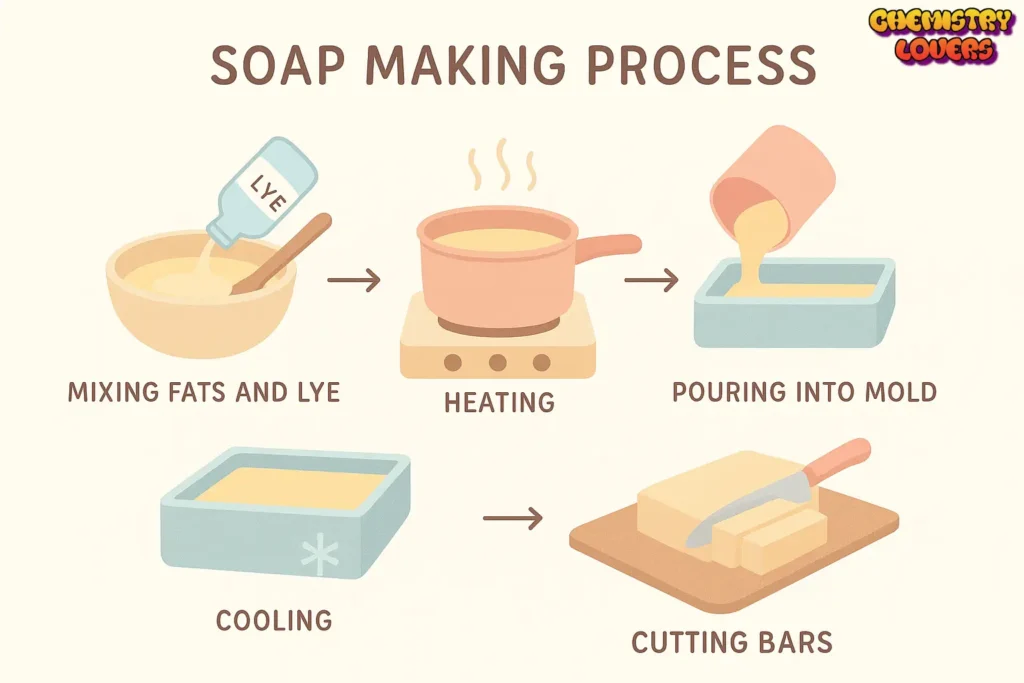
🧼 Process of Manufacturing Soap
Gather Ingredients
Oils, lye (sodium hydroxide), water, and optional fragrance or color.
Mix Lye and Water
Carefully dissolve lye in water. Always add lye to water, not the other way around.
Blend with Oils
Combine melted oils with lye water and blend until “trace” is reached.
Pour into Molds
Transfer the mixture into molds and let it set for 24–48 hours.
Cure the Soap
Allow the soap bars to cure for 4–6 weeks for a harder, longer-lasting bar.
