Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and nonmetallic gas that makes up about 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere by volume. Its chemical symbol is N, and its atomic number is 7. Nitrogen is an essential element for plant and animal life. In the free state it forms about four-fifth by volume of the air.
Next paragraph, I will describe the nitrogen cycle, its important uses, and the key properties of nitrogen, explaining why it is essential for life and various human activities.
Chief Sources.
- Air-about 78% by volume in the atmosphere.
- Sodium nitrate or chile saltpetre.
- Other nitrates mainly saltpetre, KNO3.
- Ammonium salts present in the soil.
- Animal and vegetable matter, e.g., proteins.
Nitrogen Preparation From Air.
Nitrogen can easily be separated from air. For this purpose either of the following procedures is adopted:
By fractional distillation of liquid air.
From ammonium nitrite: Ammonium nitrite liberates nitrogen on heating.
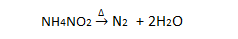
From ammonium dichromate: When solid ammonium dichromate is heated, it decomposes to liberate nitrogen.
(NH4)2 Cr2O7 → N2 + Cr2O3 +4H2O
From ammonia: Nitrogen can be obtained from ammonia by passing it over red hot cupric oxide.
2NH3 + 3CuO → 3H2O +3Cu + N2
Chemical Properties of Nitrogen.
Nitrogen is very slightly soluble in water. Under ordinary conditions, It is an inert element. It is neutral in character and neither combustible nor a supporter of combustion.
The chemical inertness of nitrogen may be attributed to a large dissociation value, 941 kj/mole. The Triple bond in nitrogen is different from other triple bonds because it does not undergo addition reaction. The following are the typical reactions of nitrogen.
(I) Combination with hydrogen
Nitrogen reacts with H2 at about 600 °C under pressure in presence of a catalyst ( Haber process for NH3).
N2 + 3H2 ⇆ 2NH3 + 141 kj/mole
Uses Of Nitrogen.
- Nitrogen is used in its fixation to ammonia, nitrates, nitric acid, fertilizers etc.
- High-temperature thermometers are filled with nitrogen to maintain temperatures up to 500 °C.
- Ammonia is synthesised from nitrogen by Haber process.
- For preservation of food in tin cans which are filled with nitrogen.
- For the manufacture of alumina by Serpek’s process.
- Nitrogen is also used to produce calcium cyanamide, commonly used as fertilizer and for the preparation of ammonia and cyanides.
- Nitrogen gas is used to provide inert atmosphere. Thus, it is used to fill electric light bulbs and to run chemical reactions in absence of air.
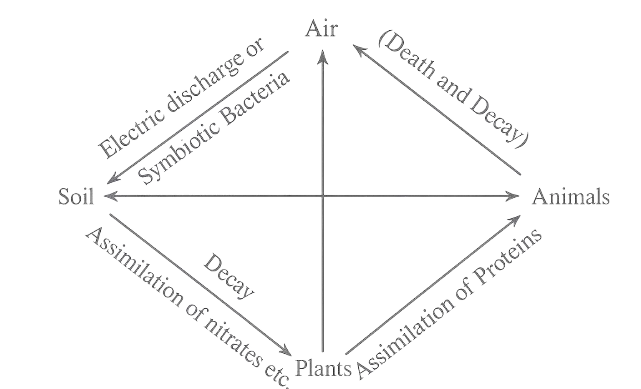
Nitrogen Cycle.
Nitrogen prèsent in the atmosphere is the source of various nitrogen containing substances indispensable to animal and vegetable life. Neither animals nor the ordinary plants can assimilate free nitrogen. Animals obtain the nitrogen supply from compounds present in plants, while plants secure the required nitrogen from nitrates present in the soil or from fertilizers. The nitrogenous compounds taken up by plants are converted into proteins in presence of light. Proteins are essential for animal life. Thus, plants form a useful link between animals and minerals or soil substances.
The source of combined nitrogen, whether present in living matter or soil is atmospheric nitrogen. The nitrogen matter in the soil (obtained from plants and dead animals, etc.) putrifies by denitrifying bacteria, liberating free nitrogen. The atmospheric nitrogen is brought back to the soil in two ways:
1. By Electric Discharge.
In presence of electric discharge nitrogen reacts with atmospheric oxygen to form water soluble oxides and oxyacids (or their salts) of nitrogen which are washed down by rain into the soil.
2. By Symbiotic Bacteria.
The leguminous plants (peas, grams, beans, etc.) live in partnership or symbiosis (living with) with certain class of bacteria present in the nodules on their roots. These bacteria get food from the plant and convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds which are assimilated by plants for their growth.
Nitrogen undergoes a never ending cycle in nature which involves continuous life and death of animals and growth, and decay of plants. The schematic diagram show in image represents the nitrogen cycle.
🧬 Nitrogen Cycle Summary Chart
| Stage | Key Process | Responsible Organisms | Main Product |
| 1 | Nitrogen Fixation | Rhizobium, lightning | NH₃ / NH₄⁺ |
| 2 | Ammonification | Decomposers | NH₄⁺ |
| 3 | Nitrification | Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter | NO₂⁻, NO₃⁻ |
| 4 | Assimilation | Plants, animals | Organic N compounds |
| 5 | Denitrification | Pseudomonas | N₂ gas |
Also Read.
- Raoult’s Law – Definition, Formula & Graph
- Metallic Solids: Properties, Bonding, and Theories Explained
- Atomic Radius – Definition, variation, Trends, and Examples
