In chemistry, the empirical and molecular formula is essential for understanding how compounds are represented. Both are closely connected, and studying the relationship between empirical and molecular formula helps in identifying the actual composition of molecules. This article will also explain the difference between empirical formula and molecular formula to make the concepts clear and easy to learn.
Empirical Formula.
A formula which indicates the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of different elements present in a compound is called an empirical formula.
Example.
CH and CH2O are empirical formulae of benzene and glucose. Certain compounds have identical molecular and empirical formula, such as H₂O, NH₃, and CCl₄.
Molecular Formula.
The Formula which represents actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule is called molecular formula.
Example.
Glucose (C6H12O6) benzene (C6H6) Ethane (C2H6) Sodium peroxide (Na2O2) and mercurous Chloride (Hg2Cl2).
Relationship Between Empirical molecular Formula.
- In case of CCl4, CH4, HCl, H2O, NH3, CO2, PCL3, H2SO4, HBr, empirical and molecular formula are identical.
- The molecular formula can be calculated by dividing molecular mass by empirical formula mass..
\text{Molecular formula} \;=\; n \times \text{Empirical formula} \\
\text{where, } \; n \;=\; \frac{\text{Molecular mass of compound}}{\text{Empirical formula mass}}
- For compounds having same molecular and empirical formula, the value for simple multiple ‘n’ is equal to1.
- Ionic compounds such as NaCl, K₂SO₄, etc., possess empirical formulas but lack molecular formulas.
Difference Between Empirical and Molecular Formula
| Empirical Formula | Molecular Formula |
| A formula which represents the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of elements in a compound. | A formula which represents actual number of atoms of element in a compound. |
| It is obtained from elemental analysis. | It is obtained by multiplying ‘n’ with empirical formula. |
| It is used for both molecular and ionic compounds. | It is used for molecular compounds. |
| Examples: CH2O and CH are empirical formulae of glucose and benzene respectively. | Examples:C6H12O6 and C6H6 are molecular formulae of glucose and benzene respectively. |
Determination of empirical Formula.
Following steps are used to determine the empirical formula:
- Calculate percentage of each element present in the compound.
- Divide percentage of each element by its atomic mass to get number of moles of each element.
- Divide number of moles of each element by least value of number of moles to get simple whole number ratio of atoms.
- If atomic ratios are in fractions, multiply these with suitable number to get simple whole number ratio.
- Write atomic ratios of elements below their symbols to get empirical formula.
Empirical formula from combustion analysis
By combustion analysis only those organic compounds can be analyzed which simply contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Combustion analysis:
The experimental procedure by which the amounts of different elements present in a compound are determined during the combustion of an organic compound in the stream of oxygen is called combustion analysis.
Process of combustion:
A known amount of organic sample is placed in a combustion tube which is fitted in a furnace. The compound is burnt in the supply of oxygen. Carbon and hydrogen are converted to CO2 and H2O. H2O and CO2 are then absorbed by Mg(CIO4)2 and 50% KOH, respectively. These absorbers are pre-weighed.
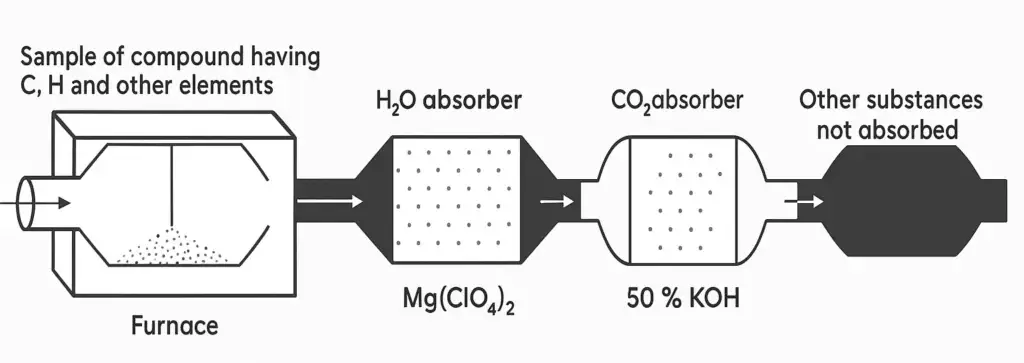
The difference in their masses give the amounts of water and CO2 respectively. From the masses, the % ages are calculated by using the following formulas.
\%\ \text{age of carbon} = \frac{\text{Mass of CO}_{2}}{\text{Mass of organic compound}} \times \frac{12}{44} \times 100 \\
\%\ \text{age of hydrogen} = \frac{\text{Mass of H}_{2}\text{O}}{\text{Mass of organic compound}} \times \frac{2}{18} \times 100
Note: % age of oxygen is calculated by subtracting sum of other % ages from 100
% age of oxygen = 100 – (% of C + % of H2)
Also Read.
- Raoult’s Law – Definition, Formula & Graph
- Metallic Solids: Properties, Bonding, and Theories Explained
- Atomic Radius – Definition, variation, Trends, and Examples
How to find Molecular Formula:
Example: The Combustion analysis of an organic compounds shows it to contain 65.44% carbon, 5.50% hydrogen and 29.06% oxygen. What is the empirical formula of the compound? The molar mass of this compound is 110.15. Calculate the molecular formula of the compound.
Solution:
Data:
% age of C = 65.44
% age of H2 = 5.50
% age of O2 = 29.06
molar Mass = 110.15
Step 1: Divide the percentage of each element by its atomic mass to get number of moles.
\[
\text{Number of moles of carbon}
= \frac{65.44 \, \text{g}}{12.01 \, \text{g/mol}}
= 5.45
\]
\[
\text{Number of moles of hydrogen}
= \frac{5.50 \, \text{g}}{1.01 \, \text{g/mol}}
= 5.45
\]
\[
\text{Number of moles of oxygen}
= \frac{29.06 \, \text{g}}{16.00 \, \text{g/mol}}
= 1.82
\]
\[
\text{Molar ratio} \quad
\begin{array}{c \; c \; c}
C & : & H \; : \; O \\
5.45 & : & 5.45 \; : \; 1.82
\end{array}
\]
Step 2: Divide the number of moles of each element by the smallest quantity which is 1.82, to get atomic ratio.
\begin{array}{c c c c c}
& C & : & H & : O \\
& \dfrac{5.45}{1.82} & : & \dfrac{5.45}{1.82} & : \dfrac{1.82}{1.82} \\
& 3 & : & 3 & : 1
\end{array}
Step 3: write atomic ratios of elements below their symbols to get the empirical formula. The given organic compounds contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 3:3:1. Therefore the empirical formula is C3H3O.
Step 4: To find out of the molecular formula, first calculate the empirical formula mass.
Empirical formula mass of C3H3O = 12 × 3 + 1 × 3 + 16 × 1 = 55.05g mol-1
Step 5: Find out value of ‘n’ by the following formula.
\[
\text{ } n = \frac{\text{Molecular mass of compound}}{\text{Empirical formula mass}}
\]
Molecular mass of the compound =110.15 g mol-1
By putting the value of empirical and molecular formula masses in above relation,
\[
n = \frac{110.15 \, \text{g mol}^{-1}}{55.05 \, \text{g mol}^{-1}} = 2
\]
Step 6: Multiply empirical formula with n. We shall get molecular formula
Molecular formula = n (empirical formula)
= 2 (C3H3O) = C6H6O2
Many structural formula are possible for this molecular formula.
