In this experiment, I will detect the presence of different lipid components in an oil by TLC. In this method, a small amount of oil is placed on a TLC plate, and a solvent helps the lipids move upward. Different lipids travel different distances on the plate, forming separate spots. By comparing these spots, we can identify the different lipid components present in the oil.
Apparatus and Chemicals.
Glass plates, capillary tubes, glass jar (developing chamber) with lid, oven, silica gel 200 mesh, solvent {(Hexane, ethyl ether, glacial acetic acid (80:20:1)}, chloroform, tocopherol, cholesterol, lecithin, phosphatidylcholine, oleic acid, vegetable oil, H2SO4 (50 % v/v) and 10 % phosphomolybdic acid solution.
Principle.
Lipids are present as a complex mixture and are first fractionated into a number of groups by solvent extraction. Determination of the compounds within each group can then be carried out by thin layer chromatography.
Procedure.
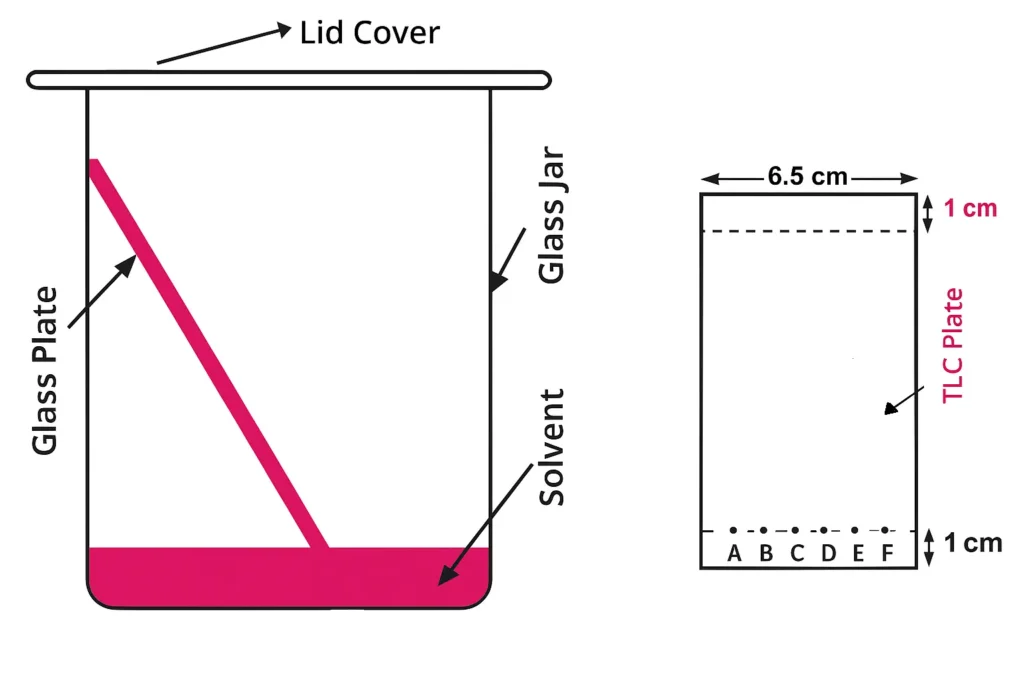
Clean the glass plate with ethanol. Make aqueous slurry of silica gel and a small quantity of calcium sulfate. Put this aqueous slurry on glass plate and use equalizer to make the surface 250 μm thick. Heat the plate at 110 °C in an oven for 1 hour and allow to cool.
Draw a line 1 cm from the bottom of the TLC plate by using a pencil and equally space 6 marks across this line for the spots. Prepare 1 % w/v solution of each lipid in chloroform (CHCl3). Spot 3 drops of the unknown (vegetable oil) sample (A) on the first mark of TLC plate by using a capillary tube. Spot known samples {tocopherol (B), cholesterol (C), lecithin (D), phosphatidylcholine (E), oleic acid (F)} on the remaining marks. Keep the spots small in diameter (2-3 mm maximum).
Prepare 25 cm3 of chromatographic solvent {(Hexane, ethyl ether, glacial acetic acid (80:20:1)} and transfer to chromatography jar. Put lid on it and wait for 20-30 minutes to saturate the internal atmosphere of the jar with solvent. Now remove the lid and place TLC plate (spotted side down) vertically in it. Again put lid on it tightly and allow separation to occur until solvent front is approx. 1 cm from the top of TLC plate. Normally it will take 30-40 minutes.
Now remove TLC plate and quickly mark the solvent front with a pencil. Allow TLC plate to dry completely on the bench (approx. 5 minutes). Spray the dry TLC plate with 10 % phosphomolybdic acid solution under the fume hood and now dry it in an oven at 70 °C for 10 minutes.
Calculate Rf, values of all the spots and identify the spot of unknown oil sample with reference to the spots of standards and their Rf values.
Note.
- Substances that are highly conjugated may be detected by fluorescence under a UV lamp (270 μm). Spraying solution is of dichloroflluorescein.
- Sulphuric acid as spraying reagent gives black spots with all organic compounds.
- lodine is another universal reagent. Solvent developed chromatogram is placed in an enclosed chamber containing a few crystals of l2. The iodine vapors will react with most of organic substances to produce yellow-brown spots on the TLC plate. The plate should be immediately marked with the pencil to indicate the position of the spots because the iodine will gradually diffuse away from the spots after removing the plate from the iodine chamber.
- The solvent is selected according to the lipids under investigation.
- Always use freshly prepared developing solvent for the experiment.
Also Read.
- Paper Chromatography of Ink – To Separate a Mixture of Various Inks
- Purify commercial NaCl by passing HCl gas
VIVA VOCE
Q. 1. Why it is necessary to keep chromatographic solvent in the developing chamber for 20-30 minutes before starting the separation?
This time period is necessary to ensure the complete saturation of inner
atmosphere of the developing chamber.
Q. 2. How can we indicate the complete saturation of developing chamber?
Use a filter paper wrapped on inner sides of the chamber to see the rising solvent vapors on filter paper.
Q. 3. What are the effects of incomplete saturation of developing chamber?
These are: Higher R, values, uneven solvent front, sharp zones having improper diffusion, short analysis time and overall inaccurate result.
Q.4 . Why CaSO4 is added to silica gel?
It acts as binding material for silica gel.
