Colligative Properties Calculator
Definition:
Those properties of solutions which depend upon the number of solute particles and not upon their nature and structure are called colligative properties.
Types of colligative properties:
There are four colligative properties of solutions:
- Lowering of vapour pressure
- Elevation of boiling point (Ebullioscopy)
- Depression of freezing point (Cryoscopy)
- Osmotic pressure
Why some of the properties are called colligative?
In order to explain the concept of colligative properties, let us take three vessels having 1000g of water in each. Dissolve 6g of urea, 18g of glucose and 34.2g of sucrose in a separate vessels. In this way we prepare 0.1 molal solution of each. Fig
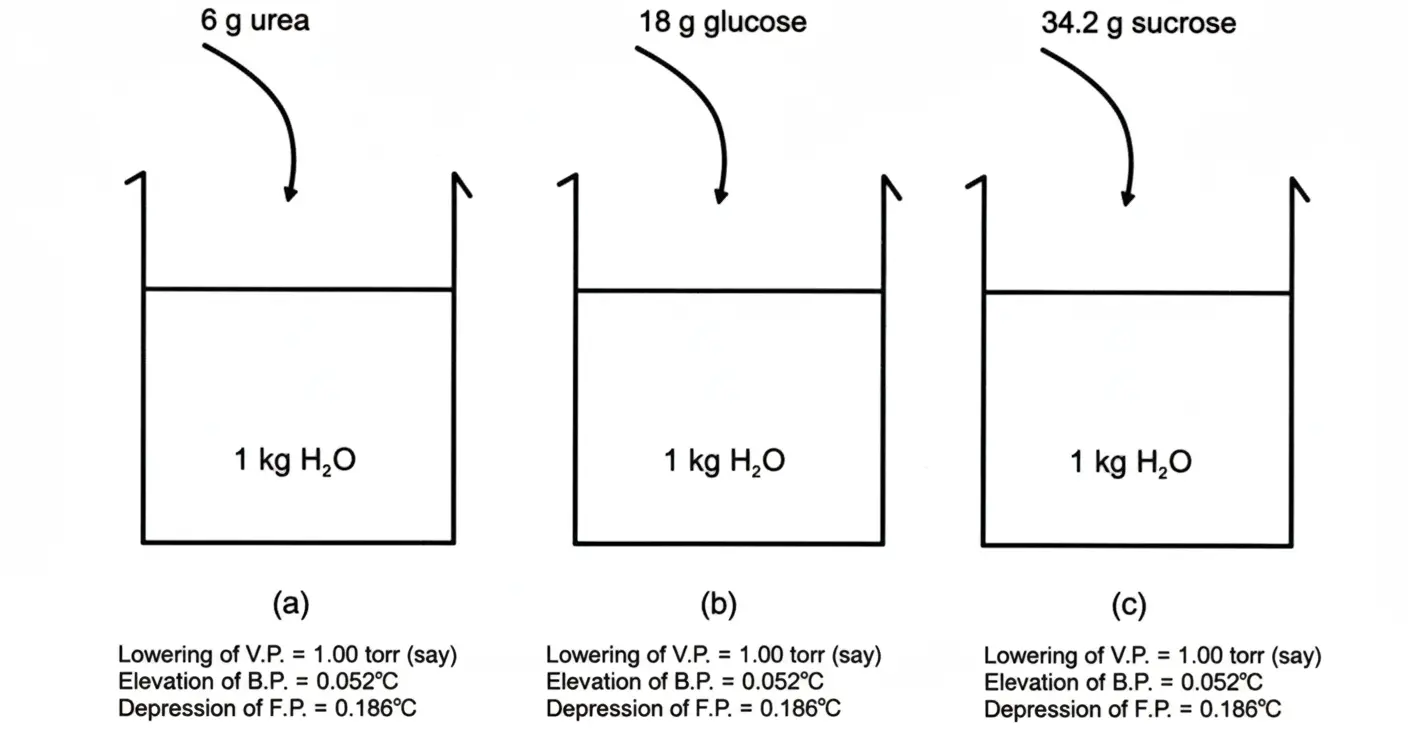
In all these solutions:
- Vapour pressures are lowered to equal extent.
- Boiling points are elevated i.e., up to 0.052°C.
- Freezing points are depressed i.e., up to 0.186°C.
No doubt, the nature of the three solutes i.e., urea, glucose and sucrose, are different, their masses are different, but the lowering of vapour pressure, elevation of boiling points and depression of freezing points are same.
The reason is that 0.1 mole of all these compounds has same number of molecules i.e., 6.02 × 1022. This is 1/10th of Avogadro’s number. These three properties depend upon the number of particles of solute and not upon their nature and structure.
